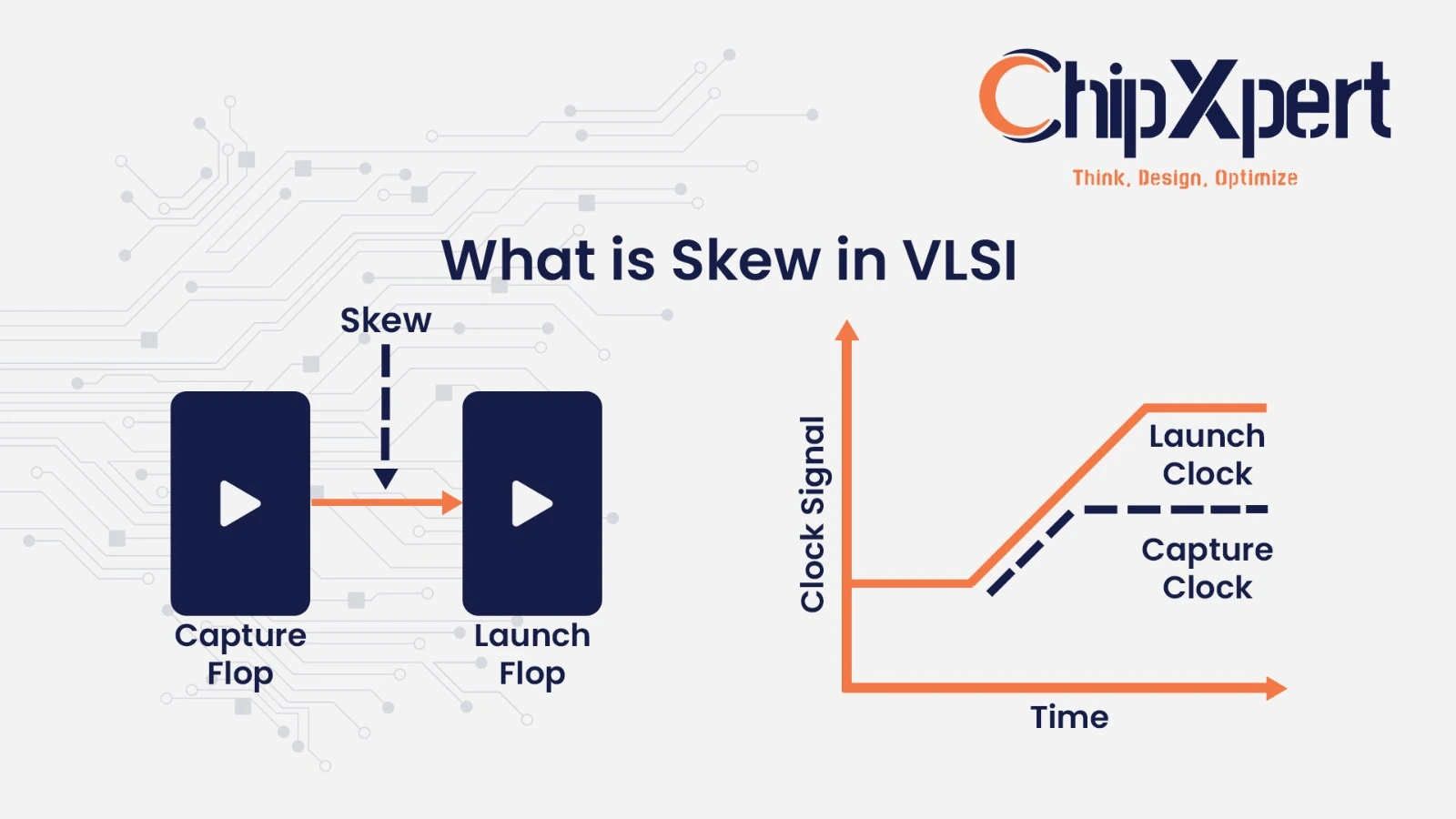


When learning VLSI design, one of the most common terms you’ll hear is what is skew in VLSI. In simple words, skew happens when the signal at the clock pin of two flip flops arrives at slightly different times. This small delay can cause timing violations if not handled properly.
Understanding skew is important for physical design and making clock trees. It affects setup timing, hold time, and chip performance
Skew in VLSI design is the difference in clock arrival time at two sequential elements. For example, if one clock edge reaches the launch flop earlier than the capture clock, there will be skew.
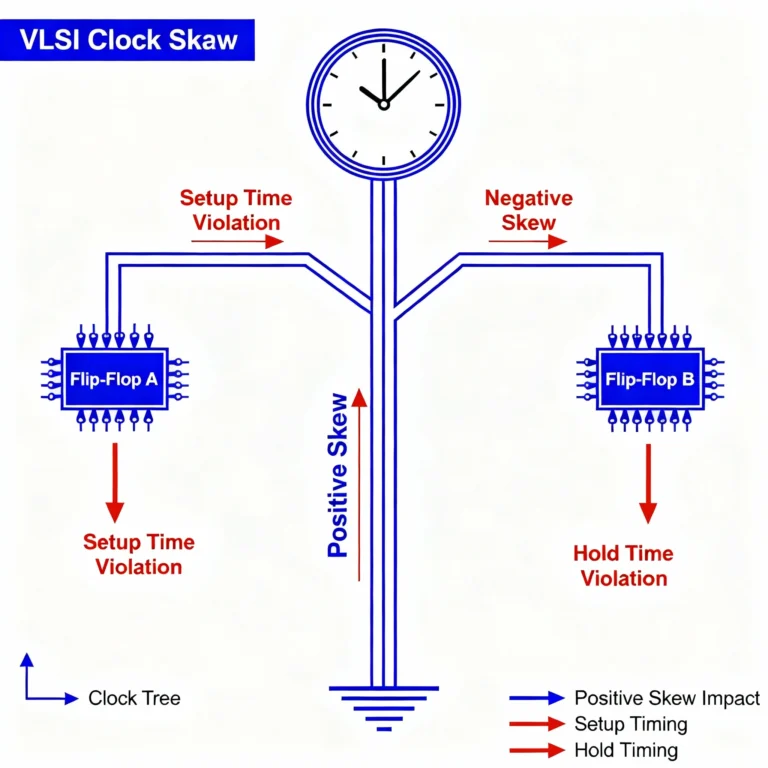
If the skew is positive, the data path gets more time for setup. If it is negative, the design might face hold issues.
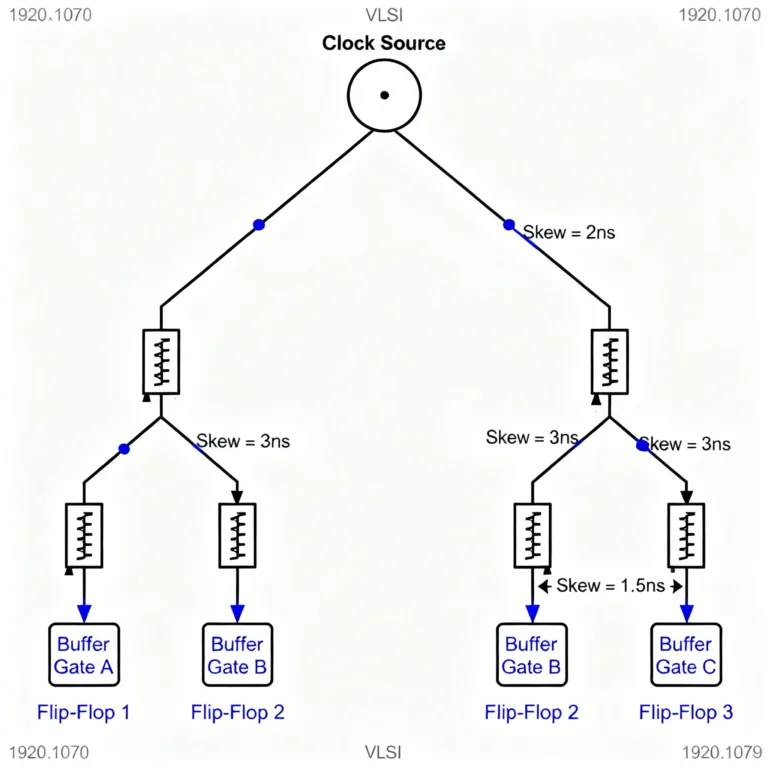
Clock skew in VLSI is simply the variation in clock arrival time across different elements. Since large chips have complex clock tree synthesis, clock edges don’t reach all flops at the same instant.
Two main types of clock skew exist:
Positive Skew – When the capture clock arrives later than the launch clock. This helps setup timing but can cause hold problems.Negative Skew – When the capture clock arrives earlier. This helps hold time but can hurt setup timing
Both need careful management to prevent timing violations.
One interesting concept is useful skew in VLSI. Instead of fighting skew, designers sometimes use it to their advantage. By deliberately adjusting clock delays, they can fix setup and hold issues.
Many designers widely use this method in advanced physical design flows.
During clock tree synthesis (CTS), the main goal is to distribute the clock with minimal skew. However, perfect zero skew is impossible. Instead, tools aim to:
CTS is an essential stage in physical design for assessing and correcting skew.
Skew directly affects how flip flops operate in a sequential circuit. If the clock’s arrival time changes a lot between the launch flop and the capture clock, it can cause wrong data storage.
Thus, skew impacts the data path, stability of signals, and synchronization of the overall design.
Designers use different techniques to minimize skew-related timing violations:
These methods ensure that chips run correctly at the required frequency without errors.
For students and engineers, understanding skew is crucial. Every VLSI design course covers it in detail because:
Now you know exactly what is skew in VLSI—the difference in clock arrival time at sequential elements. From clock skew in VLSI to useful skew in VLSI, the concept is central to chip design.
By mastering skew, you can improve setup timing. This helps you avoid hold time failures. It also ensures strong designs during physical design and clock tree synthesis.
Understanding skew is not just a theory. A practical skill that every chip designer and VLSI engineer must learn.